- Clear Command Prompt In Packet Tracer
- Packet Tracer Command Prompt Clear Screen
- Clear Command Prompt Packet Tracer
The Cisco Packet Tracer installer creates a desktop shortcut by default. If you don’t want the desktop shortcut, then you can run the following command line switches to exclude it. Cisco Packet Tracer 32-bit (EXE) PacketTracer-x.x.x-win32-setup.exe /VERYSILENT /NORESTART /MERGETASKS=!desktopicon.
Cisco ASA includes a very nice feature since the 7.2(1)-release; packet-tracer.
Start studying Basic Cisco Packet Tracer Commands. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Configuring FTP Server explained using CISCO Packet Tracer.
In short, you can inject and trace a packet as it progresses through the security features of the Cisco ASA appliance and quickly determine wether or not the packet will pass.
I often use it to verify traffic passing through firewall rules, NAT-rules and VPN, but its uses is not limited to these three common troubleshooting steps.
Command structure
packet-tracer input <source interface> <protocol> <source IP> <source port> <destination IP> <destination port> [detailed]
Useful commands to be used in conjunction with the packet-tracer is “clear conn” and “clear xlate” to clear connection table and NAT-table.
- NOTE: You will obviously kill all IP-sessions running through the appliance using the clear-commands. So use it at your own risk and don’t blame me if your users comes running after you wielding pitch forks and torches. ,)
Example
Following is an example of a packet-trace to a web-server through a VPN-tunnel, without the “detailed”-option.
My comments in red.
CiscoASA# packet-tracer input inside tcp 10.20.30.40 54444 10.50.60.70 http
Phase: 1
Type: ACCESS-LIST
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Implicit Rule
Additional Information:
MAC Access list
Phase: 2
Type: FLOW-LOOKUP
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Found no matching flow, creating a new flow
Phase: 3
Type: ROUTE-LOOKUP
Subtype: input
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
in 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 outside
Phase: 4
Type: ACCESS-LIST
Subtype: log
Result: ALLOW
Config:
access-group ACL-inside-in in interface inside
access-list ACL001f-inside-in extended permit ip any any
Additional Information:
Phase: 5
Type: IP-OPTIONS
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Phase: 6
Type: INSPECT
Subtype: np-inspect
Result: ALLOW
Config:
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect http
service-policy global_policy global
Additional Information:
Phase: 7
Type: NAT-EXEMPT
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
nat-control
match ip inside 10.20.30.0 255.255.255.0 outside 10.40.50.0 255.255.255.0
NAT exempt
translate_hits = 51480, untranslate_hits = 854212
Additional Information:
THE TRAFFIC IS NOT NATED, EVEN THOUGH PHASE 8/9 RESULTS YIELDS RESULT “ALLOW”.
Phase: 8
Type: NAT
Subtype: host-limits
Result: ALLOW
Config:
nat (inside) 1 access-list inside_nat_outbound
nat-control
match ip inside 10.20.30.0 255.255.255.0 outside host 10.2.2.10
dynamic translation to pool 1 (200.200.200.200 [Interface PAT])
translate_hits = 0, untranslate_hits = 0
Additional Information:
Phase: 9
Type: NAT
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
nat (inside) 1 10.20.30.0 255.255.255.0
nat-control
match ip inside 10.20.30.0 255.255.255.0 outside any
dynamic translation to pool 1 (200.200.200.200 [Interface PAT])
translate_hits = 3205631, untranslate_hits = 383007
Additional Information:
Phase: 10
Type: VPN
Subtype: encrypt
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information: TRAFFIC MATCHES VPN AND WILL BE ENCRYPTED
Phase: 11
Type: VPN
Subtype: ipsec-tunnel-flow
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Phase: 12
Type: IP-OPTIONS
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Phase: 13
Type: FLOW-CREATION
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
New flow created with id 10948889, packet dispatched to next module
Result:
input-interface: inside
input-status: up
input-line-status: up
output-interface: outside
output-status: up
output-line-status: up
Action: allow FINAL ACTION IS ALLOW WHICH MEANS THE PACKET IS NOT STOPPED IN CONFIGURATION AND WILL BE PASSED ON.
If I try to run the same command again, we will see it matches an existing flow in phase 2 and promptly passed on.
CiscoASA# packet-tracer input inside tcp 10.20.30.40 54444 10.50.60.70 http
Phase: 1
Type: ACCESS-LIST
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Implicit Rule
Additional Information:
MAC Access list
Phase: 2
Type: FLOW-LOOKUP
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Found flow with id 10953078, using existing flow
Result:
input-interface: inside
input-status: up
input-line-status: up
Action: allow
Packet tracer via ASDM / GUI
You can also find the packet-tracer is ASDM via “Tools > Packet Tracer”:
Packet Tracer Cisco CLI Commands list
Here is the detailed Cisco router configuration commands list, which can be implemented with packet tracer. Packet tracer is a network simulator used for configuring and creating the virtual cisco devices and network. There are also some other similar software but Cisco IOS output will be same on all simulators.
Related Article: PowerShell vs Command prompt
To configure any device in packet tracer you are required to open or access its CLI. You can do it by clicking any device and then navigating to CLI tab. Once you are at CLI you can perform all Cisco Commands here.
Cisco IOS supports numerous command modes which can be practice with packet tracer, followings are the main command modes of cisco CLI with specific commands to navigate from one mode to other.
| Mode | Symbol | How to access this mode | Command for leaving this mode |
| User EXEC Mode | Router > | Default mode after booting. Press enter for accessing this. | Use exit command |
| Privileged EXEC mode | Router # | Use enable command from user exec mode for entering into this mode | exit |
| Global Configuration mode | Router(config)# | Use configure terminal command from privileged exec mode | Exit or Ctrl+Z for user EXEC mode |
| Interface Configuration | Router(config-if)# | Use interface <interface name+number> command from global configuration mode | Use exit command to return in global mode |
| ROMMON | ROMMON > | Enter reload command from privileged exec mode. Press CTRL + C key combination during the first 60 seconds of booting process. | Use exit command. |
IOS commands are not case sensitive it means that you can use them in uppercase, lowercase, or mixed case, but passwords are case sensitive. Therefore make sure you type it in correctly. In any mode, you can obtain a list of commands available on that mode by entering a question mark (?).
How to Change the Cisco Router name
You can change the cisco router name by using command hostname in global configuration mode.
How to set the Enable password:
You can set the password for protecting enable mode by following command: (Following command will set the password to cisco)
How to set the telnet password on Cisco:
You can access the cisco router remotely by VTY lines, these are the Virtual Terminal lines for access router, you can set password on these line by using the following commands:
Router(config)#line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)#password Cisco
Router(config-line)#no login
Above command will set the telnet password to “Cisco”.
How to set the IP address to Cisco interface:
You can set the IP address to any Cisco device interface by using the following commands:
Router(config)#interface <interface name&number>
Router(config-if)#ip address <IP address> <subnet mask>
How to enable a port or interface
Router(config-if)#no shut
Example:
How to check the IP address of all interfaces:
You can use the “show ip interface brief” command in Privileged EXEC mode for checking the IP address of all interface of Cisco device.
How to save the configurations:
You can use the following command for router configuration to Nvram for use at next boot up
Router#copy running-config startup-config
How to configure the access-list on Cisco:
You can configure the access-list on cisco by using following commands:
Router(config)#Access-list <number> <permit|deny> <ip> <mask>
Router(config-if)#ip access-group <number> <in|out>
OR
Router(config)#Access-list <number> <permit|deny> <protocol> <from ip and mask> <to ip and mask> <port number>
Router(config-if)#
Command Example:
Router(config)#access-list 2 deny 192.168.0.33 0.0.0.255
Router(config)#interface fastEthernet 4/0
Router(config-if)#ip access-group 2 in
How to configure the default route on Cisco:
Following command will set the default route to 10.10.10.101.
Router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.10.101
How to create a static route on Cisco router
Router(config-router)#ip route [destination_network] [mask] [next-hop_address
you can set a static route by using above command example is also given below:
Router(config-router)#ip route 192.132.23.1 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.1
—————————
——————-
Clear Command Prompt In Packet Tracer
| RIP Configuration Commands | |
| Commands | Details |
| Router(config)#Router rip | Enable RIP routing on router. |
| Router(config-router)#Network <network ip address> | Define the network which you want to advertise in RIP. E.g. Network 192.168.88.0 |
| OSPF Configuration Commands | |
| Router(config)#Router ospf <process-id> | Enable OSPF routing on router. Process-id is any number & must be same for all networks in AS. |
| Router(config-router)#Network < ip address> <wild cardmask> | IP address is the IP of network which will be advertise in OSPF and wild card mask will represent the network bits. E.g. network 192.168.1.0 0.0.255.255 is equilent to 192.168.0.0/16 |
| EIGRP configuration Commands | |
| Router(config)#Router eigrp <AS number> | AS number is a number must be same for networks which are desired to connect with each other. E.g. Router eigrp 1 |
| Router(config-router)#Network < ip address> | Advertise network in EIGRP |
| Router(config-router)#no auto-summary | Disable auto summay |
How to set banner message on Cisco Device:
banner motd <banner start identification> banner message <banner end identification>
Command Example:
Packet Tracer Command Prompt Clear Screen
banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
Clear Command Prompt Packet Tracer
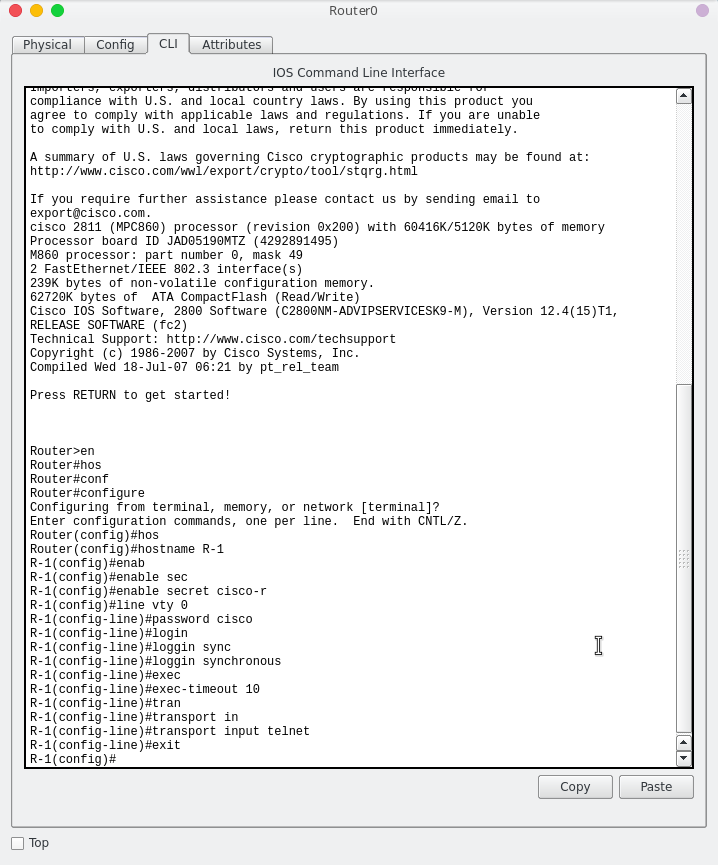
Above command with set the banner to “Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited”
Famous Show Commands in Privileged EXEC Mode
You can run all these command for checking different setting of Cisco device in privileged EXEC mode:
Show Version
Show running-config
Show Vlan
Show mac-address-table
Show clock
Show privilege
Show interface <interface name>
show ip route
Show controllers
show cdp neighbors
Show memory
Show protocols
Show startup-config
Show Flash
Show spanning-tree
Verifying Commands for Network Connectivity
You can use these commands to verify network connectivity for your router
router# enable
router# ping [ip-address | hostname]
Command Example:
router# ping 192.168.3.1
(A reply response from host 192.168.3.1 will verify the connectivity)
How to telnet any host:
telnet {ip-address | hostname}
e.g. router# telnet 192.168.3.1
Related Article: NMAP Commands Linux